
Minnesota is home to a diverse range of ecosystems.
Read more about Minnesota’s natural areas below and find out about opportunities to participate in this state.
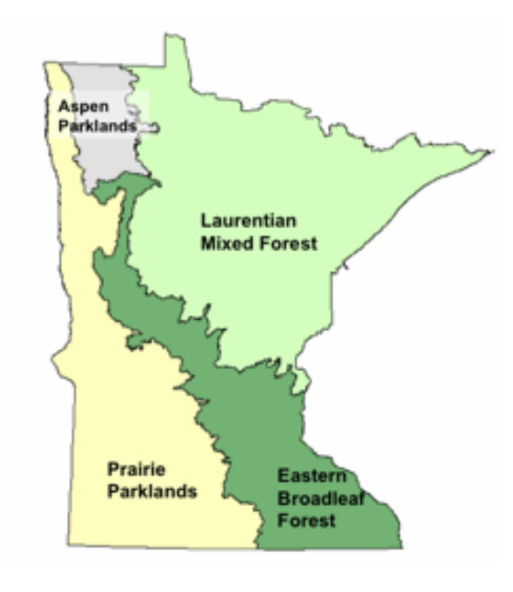
Major Ecosystems in Minnesota
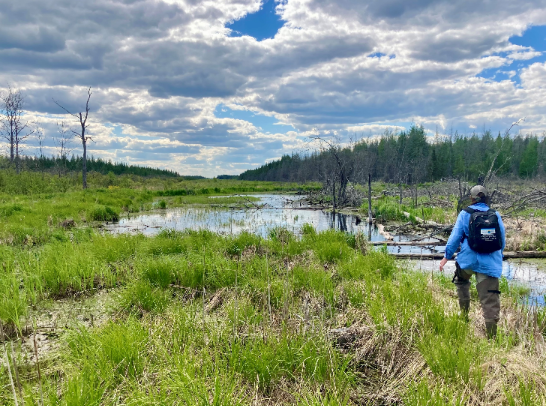
Laurentian Mixed Forest
Northeastern Minnesota is dominated by the Laurentian Mixed Forest. For many, this is synonymous with the north woods or boreal forest. Here, you’ll mostly find aspen, pine, spruce and fir, with pockets of northern hardwoods caused by changes in climate.
Eastern Broadleaf Forest
The Eastern Broadleaf Forest province runs in a narrow band through the center of the state. As the name suggests, you’ll find fewer conifers in this area and more hardwoods like oaks, hickories, maples and basswood. This province is home to Minnesota’s famous Big Woods—an area west of the Twin Cities that contained over 3,000 square miles of deciduous forest before extensive settlement and development. Only a small portion of the original Big Woods remains.
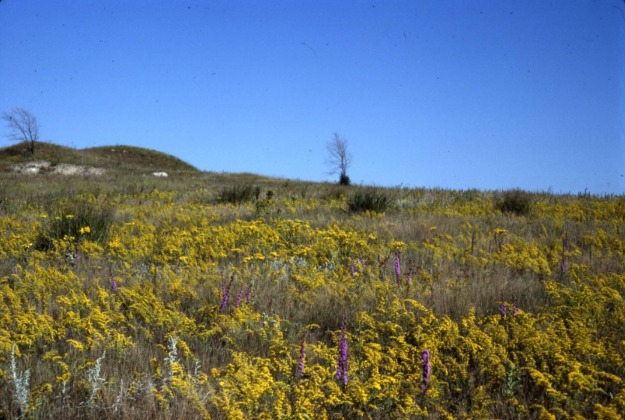
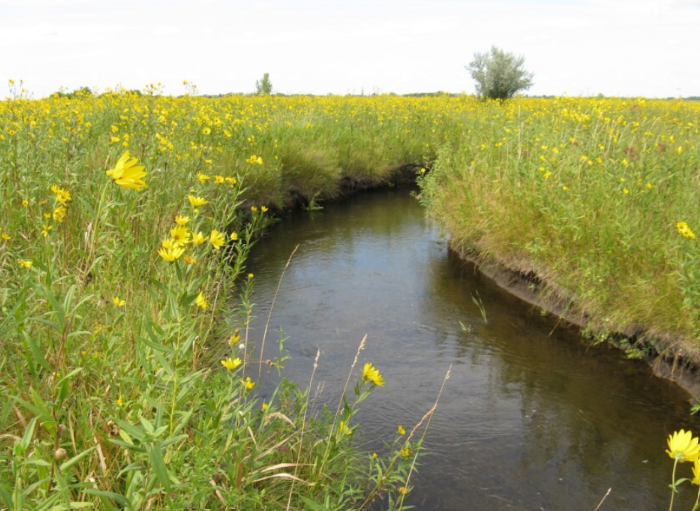
Prairie Parkland
The Prairie Parkland province is in southern and western Minnesota. Once dominated by native prairie, this province now includes some of Minnesota’s most productive agricultural land. A few remnants of the prairie still exist, mostly in state parks and other protected areas.
Tallgrass Aspen Parklands
The Tallgrass Aspen Parklands province extends into northwestern Minnesota from the north. It’s characterized by an open aspen savanna with tallgrass prairie vegetation mixed in. Read here for a description from University of Mn Extension.

Organizations for Restoration in Minnesota:
Resources for Restoration Practitioners and Students:
- Minnesota Landscape Arboretum
- PRRSUM
- University of Minnesota, online ecological restoration classes
- Minnesota BWSR,


arboretum
